SaaS subscription pricing comparison enterprise insights
SaaS subscription pricing comparison enterprise opens the door to a world where businesses can navigate the diverse pricing models available in the Software as a Service landscape. With various options tailored to fit different enterprise needs, understanding these pricing strategies is essential for making informed decisions and maximizing value. From tiered systems to flat-rate options, each model presents unique benefits and considerations that can significantly impact a company’s bottom line.
Exploring the intricacies of SaaS pricing not only highlights the competitive landscape but also equips enterprises with the knowledge to adapt their strategies. As market demands and technological advancements evolve, having a firm grasp of how pricing models work can lead to better negotiations and ultimately, enhanced relationships with providers.
Overview of SaaS Subscription Pricing Models: SaaS Subscription Pricing Comparison Enterprise
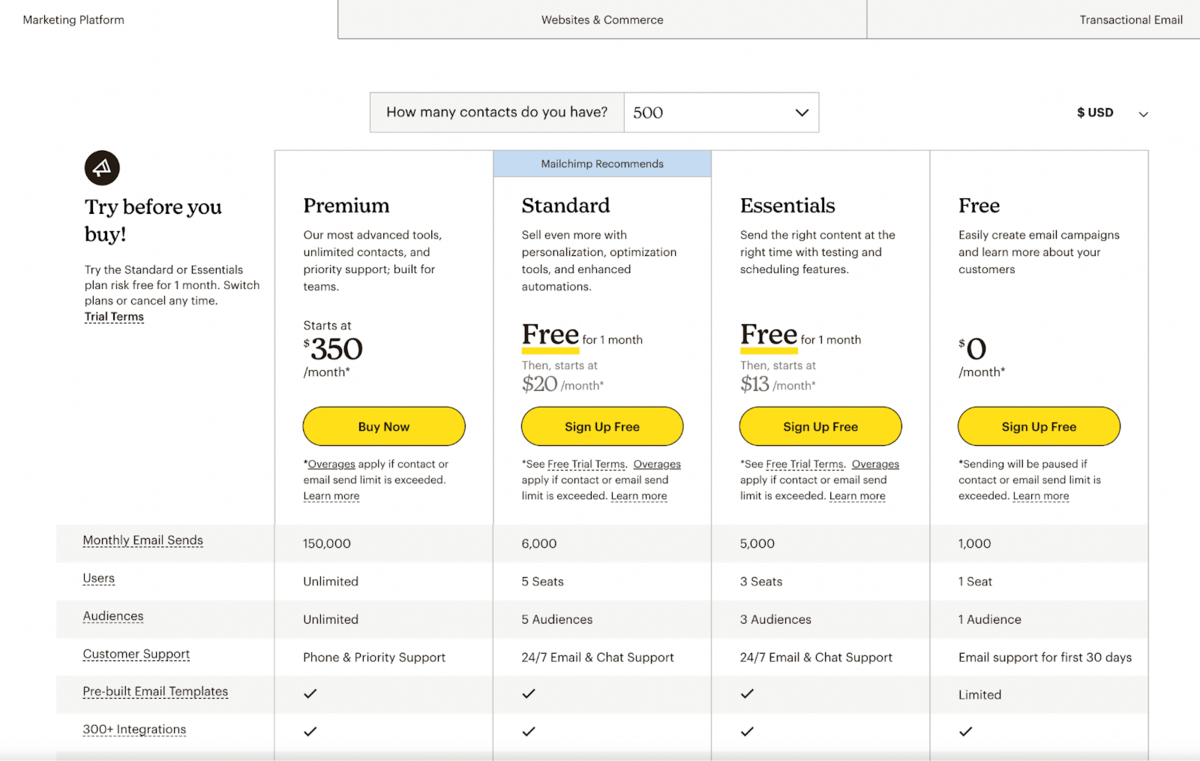
SaaS (Software as a Service) subscription pricing models play a crucial role in how enterprises select and utilize software solutions. Understanding these models is essential for businesses aiming to optimize their software expenses while meeting varying operational demands. The most prevalent pricing models in the SaaS landscape include tiered, flat-rate, and per-user pricing.The choice of a pricing model can deeply influence an enterprise’s budgeting and software scalability.
Each model comes with its own set of advantages and challenges, making it imperative for organizations to align their software purchases with their specific business needs and growth trajectories.
Tiered Pricing Model
The tiered pricing model offers different levels of service or features at varying price points, allowing businesses to choose a tier that best fits their needs. This model can cater to small businesses and large enterprises alike by providing flexibility and scaling options.
- Benefits:
- Flexibility to choose features relevant to business size and needs.
- Ability to scale up services as the company grows without facing sudden cost hikes.
- Drawbacks:
- Can lead to confusion if the tier differences are not clearly defined.
- Potential for overspending if a higher tier with unnecessary features is chosen.
Flat-Rate Pricing Model
In a flat-rate pricing model, enterprises pay a single price for access to the software, regardless of usage levels or features. This model is straightforward and predictable, making budgeting simpler for organizations.
- Benefits:
- Simple pricing structure that makes budgeting predictable.
- No hidden fees or unexpected charges, providing transparency.
- Drawbacks:
- May not accommodate the diverse needs of all users within an enterprise.
- Could result in paying for features that are not utilized.
Per-User Pricing Model
The per-user pricing model charges enterprises based on the number of users accessing the software. This model is particularly appealing to organizations with fluctuating employee counts or those looking to control costs closely.
- Benefits:
- Cost-effective for businesses with fewer users, offering greater affordability.
- Encourages organizations to manage user access efficiently.
- Drawbacks:
- Can become costly as the number of users increases.
- May lead to businesses limiting user access to cut costs, potentially hindering collaboration.
“Choosing the right SaaS pricing model is fundamental to ensuring that software solutions align with both operational needs and budgetary constraints.”
Different pricing models cater to various enterprise needs, with tiered pricing offering scalability, flat-rate pricing providing simplicity, and per-user pricing allowing cost control. Organizations must evaluate their unique situations, projected growth, and budget constraints to select the most suitable model for their SaaS subscriptions.
Factors Influencing SaaS Pricing in Enterprises
In the dynamic landscape of Software as a Service (SaaS), pricing strategies are influenced by a multitude of factors. Understanding these elements is crucial for enterprises to navigate their subscription models effectively. Pricing is not merely about setting a number; it reflects various influences ranging from market trends to customer demographics. Key factors affecting SaaS pricing include market demand, competition, and the features of the service offered.
As demand for specific software solutions rises, providers may adjust their pricing to reflect the perceived value and urgency of adoption. Similarly, competition plays a critical role—companies must remain competitive while still covering costs and ensuring profitability. The features that a SaaS solution provides can also significantly impact pricing; comprehensive offerings that address specific business needs often command higher prices.
Market Demand and Competition
Market demand influences how companies position their products and set their prices. When a specific solution is sought after, the pricing can be adjusted upwards to capture additional value. Conversely, during periods of low demand, businesses may choose to lower prices to stimulate interest. Competition requires careful consideration as well. SaaS providers analyze competitor pricing and offerings to ensure they remain appealing to potential customers.
The following are important aspects influenced by market demand and competitive landscape:
- Value Proposition: The clarity and strength of a product’s value proposition can dictate pricing strategies. Enterprises that clearly communicate the benefits of their solution can often command higher prices.
- Market Entry Timing: New entrants in a saturated market may adopt a penetration pricing strategy, offering lower prices initially to attract customers.
Customer Size and Industry Influence
The size of the customer and the industry they operate within also influence pricing strategies considerably. Larger enterprises often have greater budgets and specific needs that can justify higher expenditure for tailored solutions. In contrast, small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) might have tighter budgets, prompting SaaS providers to create tiered pricing models catering to varied economic capabilities.For example, enterprise-level clients may require advanced features such as enhanced security measures and dedicated support, while SMBs might prioritize basic functionalities.
The following points further highlight this differentiation:
- Industry-Specific Needs: Some industries, like healthcare or finance, may require compliance features that can raise pricing due to their critical nature.
- Volume Discounts: Larger customers might receive discounts based on volume commitments, influencing overall pricing strategies.
Implementation and Support Costs
Implementation and support costs are integral to the overall pricing structure of SaaS products. These costs can vary significantly based on the complexity of the software and the level of customer support provided. A seamless onboarding process and ongoing support are essential for customer satisfaction, but they also incur expenses that need to be accounted for in pricing.The importance of these costs is illustrated by the following considerations:
- Setup Fees: Many SaaS providers charge initial setup fees to cover the costs of deploying the software within a customer’s environment.
- Support Tiers: Different levels of customer support (e.g., standard vs. premium) can lead to varied pricing, allowing customers to choose options that fit their needs and budget.
Understanding these factors allows enterprises to make informed decisions regarding their SaaS pricing strategies, ensuring alignment with both market conditions and customer expectations.
Competitive Analysis of SaaS Pricing
In today’s rapidly evolving enterprise landscape, understanding the pricing structures of SaaS providers is essential for making informed decisions. Competitive pricing analysis allows businesses to gauge where they stand in comparison to their competitors, which can significantly influence pricing strategies. A thorough examination of leading SaaS providers’ pricing models offers insights into common practices and potential gaps in the market.The following section presents a detailed breakdown of the pricing offerings from some of the leading SaaS providers in the enterprise sector.
This comparison highlights various tiers, core features, and typical price points.
Comparison of Pricing Structures
A well-structured comparison of SaaS pricing can illuminate the strategies employed by competitors, allowing businesses to optimize their own pricing approaches. Below is a table that summarizes the pricing tiers and offerings of several prominent SaaS providers.
| Provider | Basic Tier | Standard Tier | Premium Tier | Enterprise Tier |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | $15/month | $50/month | $100/month | Contact for pricing |
| Company B | $20/month | $60/month | $120/month | $250/month |
| Company C | $10/month | $40/month | $90/month | Contact for pricing |
| Company D | $25/month | $70/month | $150/month | Custom pricing available |
The table above showcases various pricing tiers, with Company A offering a strong mid-range option at $50/month, while Company B leads with slightly higher pricing across tiers. Notably, Company C’s entry-level option at $10/month is attractive for startups and smaller enterprises, demonstrating the competitive nature of pricing in the SaaS industry.
“Understanding competitor pricing helps refine your own pricing model, ensuring you remain competitive while delivering value.”
The pricing strategies of competitors significantly shape how businesses position their offerings. A deep dive into competitors’ features and pricing can reveal opportunities for differentiation, encouraging enterprises to adjust features or pricing tiers to better meet market demands. For instance, if a competitor offers a robust analytics feature at a particular price point, it may prompt you to enhance your analytics capabilities or reconsider your pricing strategy to include or exclude similar features.By continuously monitoring these pricing structures, enterprises can remain agile, ensuring they meet customer needs while staying competitive in the marketplace.
Case Studies of SaaS Pricing Implementation
In the rapidly evolving landscape of SaaS, several enterprises have effectively implemented innovative pricing strategies that not only enhanced their revenue but also their customer satisfaction. By analyzing these real-world examples, we can gain insight into the practical applications of various SaaS pricing models and the subsequent impacts on their operations.One notable success story is that of Adobe, which transitioned from a traditional software licensing model to a subscription-based SaaS model with Adobe Creative Cloud.
This shift allowed customers to pay a monthly fee for access to the suite of creative applications instead of a one-time purchase. The impact was significant; Adobe reported a 22% increase in annual revenue following the implementation of this model. The subscription approach not only provided consistent cash flow but also allowed Adobe to innovate and update applications regularly, keeping customers engaged and satisfied.
Key Changes in Pricing Strategy
The shift to a subscription model often involves several key changes in pricing strategies. For companies like Adobe, these changes included:
- Tiered Pricing: Adobe introduced multiple tiers of service, catering to different user needs—from individuals to large enterprises—making it easier for customers to select a plan appropriate for their use case.
- Freemium Model: Providing a basic version for free helped to attract a larger user base, some of whom later converted to paid subscriptions for additional features.
- Usage-Based Pricing: In some cases, companies implemented pricing based on the volume of usage, which can align costs with actual user engagement and consumption.
The changes made by Adobe exemplify how a well-thought-out pricing strategy can lead to substantial growth and enhanced user loyalty.
Lessons from Failed Pricing Strategies
Not all pricing strategies yield positive outcomes. Several companies have faced challenges when implementing SaaS pricing models. For instance, the case of Box, a cloud content management platform, serves as a cautionary tale. Initially, Box adopted a simplistic flat-rate pricing model, which failed to account for the diverse needs of its enterprise customers. This approach limited the company’s ability to cater to larger enterprises that required more customization and flexibility in their subscriptions.The failure to effectively segment the market and understand the unique requirements of various customer bases highlighted the importance of adaptability.
Companies should avoid:
- Overcomplicating Pricing Tiers: Too many options can confuse customers, leading to decision fatigue and potential loss of sales.
- Neglecting Customer Feedback: Failing to actively seek and incorporate customer feedback can result in a disconnect between what customers want and what is being offered.
- Ignoring Market Trends: Staying uninformed about competitor strategies and market demands can lead to obsolete pricing models that do not resonate with customers.
Understanding the market and customer needs is essential for a successful SaaS pricing strategy.
The experiences of companies like Adobe and Box emphasize the need for a balance between strategic pricing and customer-centric approaches, ensuring that their SaaS offerings are both appealing and relevant to their target audiences.
Customer Perception of SaaS Pricing
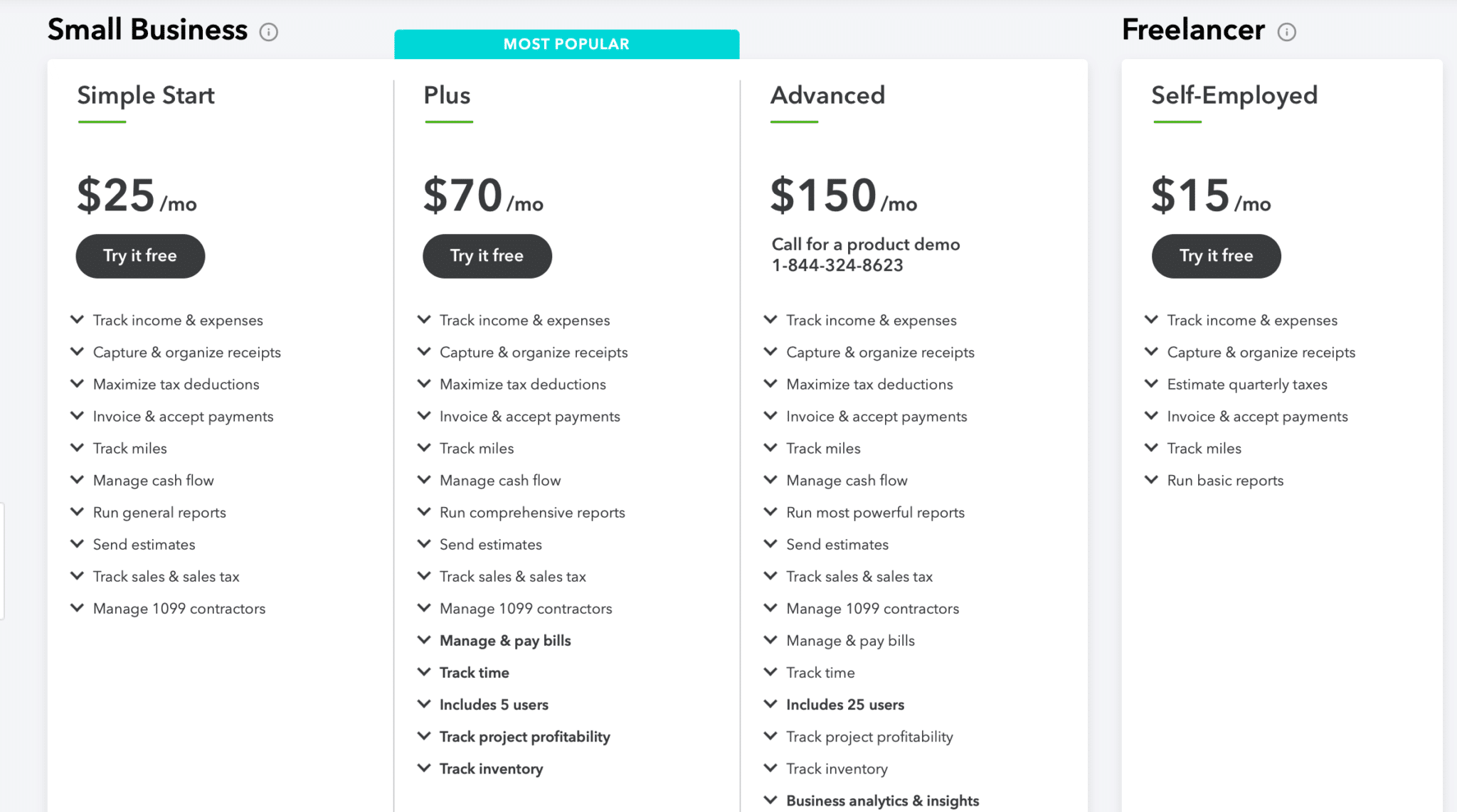
Understanding customer perception of pricing in the SaaS landscape is crucial for businesses aiming to enhance their offerings and retain clientele. Customers often form opinions based on their experiences and feedback, which can significantly influence a company’s pricing strategies. Recognizing how clients perceive value can help SaaS providers optimize their pricing models to better align with market expectations and enhance user satisfaction.Customer feedback serves as a vital tool in shaping pricing strategies in the SaaS space.
By actively seeking and integrating customer insights, businesses can adapt their pricing to better reflect the perceived value of their services. This responsive approach not only fosters loyalty but can also lead to increased customer acquisition through positive word-of-mouth.
Methods for Gauging Customer Satisfaction with Pricing
Gauging customer satisfaction with pricing involves various methodologies that provide actionable insights. Employing surveys and analyzing usage data are two effective methods to understand customer sentiment towards pricing. Surveys can be tailored to collect specific feedback regarding pricing perceptions, willingness to pay, and the perceived value of features. These surveys can be distributed periodically to ensure that the feedback is relevant and timely.
Usage data also plays an essential role in understanding how customers interact with the service and its pricing. Analyzing which features are most utilized can inform pricing strategies, allowing companies to consider tiered pricing or bundling options that reflect the actual use case of the product.Here are some common methods to gauge customer satisfaction with SaaS pricing:
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys: Direct feedback about pricing and value perception through structured surveys.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): A metric that assesses customer loyalty and satisfaction, indirectly reflecting on pricing.
- Usage Analytics: Insights derived from monitoring feature usage to determine the perceived value of the service.
- Focus Groups: Engaging a select group of customers to discuss and provide feedback on pricing strategies.
- Customer Interviews: One-on-one discussions to understand personal experiences and sentiments regarding pricing.
Organizing customer testimonials and reviews regarding pricing can provide a clearer picture of how pricing is perceived in the market. Testimonials reflect real user experiences and can be a powerful tool for marketing and strategy adjustment. Below is a collection of insights from customers on their pricing experiences:
- “The tiered pricing structure makes it easy for us to choose a plan that fits our budget.” – Tech Startup CEO
- “I feel that the pricing is fair given the value we receive from the features.” – Operations Manager
- “We switched from a competitor because their pricing was not transparent.” – Marketing Director
- “I wish there were more options for customization in the pricing plans.” – Product Owner
Future Trends in SaaS Pricing

As the SaaS landscape continues to evolve, so do pricing strategies that accommodate changing customer needs and market dynamics. Future trends in SaaS pricing are increasingly shaped by technological advancements, user expectations, and competitive pressures. This section explores these emerging trends and their implications for enterprises.
Emerging Pricing Strategies, SaaS subscription pricing comparison enterprise
Various innovative pricing strategies are expected to emerge as the SaaS market matures, focusing on flexibility and user-centric approaches. These strategies include:
- Usage-based Pricing: This model charges customers based on their actual usage rather than a flat fee. As companies seek to align costs with value derived, this approach offers potential for both scalability and affordability.
- Freemium Models: Providing a basic version for free while charging for premium features encourages widespread adoption and allows users to experience the product before committing financially.
- Tiered Pricing: Offering multiple tiers with varying features can cater to different customer segments, allowing enterprises to choose a plan that best fits their needs.
“The future of SaaS pricing will revolve around user-centric models that align cost with actual usage and perceived value.”
Usage-Based Pricing Implications
The shift towards usage-based pricing is gaining momentum, especially in sectors where consumption can be easily measured. This model offers distinct advantages, including:
- Cost Control: Enterprises can manage expenses more effectively as they only pay for what they use, which aligns expenses with business growth.
- Flexibility: Companies can scale their usage up or down according to changing demands, preventing overpayment for unused features.
- Customer Retention: By allowing businesses to adjust their spending, usage-based pricing can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, as they feel they are receiving fair value.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Pricing Models
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are poised to revolutionize pricing models within the SaaS industry. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to optimize pricing strategies in real-time. Important aspects include:
- Dynamic Pricing: AI algorithms can adjust prices based on demand fluctuations, competitor pricing, and customer behavior, ensuring that prices are both competitive and profitable.
- Personalized Pricing: Leveraging machine learning, SaaS companies can tailor pricing packages to individual customer needs, enhancing the value proposition.
- Predictive Analytics: AI can forecast customer usage patterns and preferences, enabling businesses to proactively adjust pricing structures to maximize revenue.
“AI and machine learning will empower SaaS companies to implement dynamic and personalized pricing models that respond to market changes in real-time.”
Negotiation Strategies for Enterprise SaaS Pricing
In today’s competitive landscape, negotiating SaaS pricing effectively is crucial for enterprises seeking to maximize value while minimizing costs. Securing a favorable deal can significantly impact the overall budget and resource allocation within an organization. Understanding the nuances of negotiation can lead not only to better pricing but also to enhanced terms and conditions that align with business goals.Building a successful negotiation strategy begins with knowing what elements to prioritize.
Elements such as service level agreements (SLAs), contract duration, and scalability options should be part of your conversation. A well-structured approach can empower enterprises to achieve mutually beneficial agreements that promote long-term partnerships with SaaS providers.
Effective Negotiation Tactics
Employing effective tactics during negotiations can substantially influence the final pricing and conditions. Here are some essential strategies to consider:
- Do Your Research: Understanding the market landscape and pricing benchmarks gives you leverage in negotiations. Gather data on competitors and their offerings to strengthen your position.
- Leverage Volume Commitments: If your enterprise can commit to a higher volume, use this as a bargaining chip. Providers often offer better pricing for larger contracts.
- Engage Multiple Vendors: Creating competition among vendors can push them to offer more favorable terms. Presenting proposals from multiple providers fosters a sense of urgency and can lead to better pricing.
- Understand the Provider’s Constraints: Knowing the provider’s limitations can help you propose realistic demands that they are more likely to agree to. This fosters a cooperative rather than adversarial negotiation environment.
- Negotiate for More Than Price: Consider requesting additional features, enhanced support, or flexible payment terms as part of your negotiation package. These elements can provide substantial additional value.
Checklist for Negotiating Terms and Pricing
Having a checklist can streamline the negotiation process and ensure all critical aspects are addressed. Below is a comprehensive checklist for effective negotiation:
- Define Your Needs: Clearly Artikel the features and services necessary to meet your business objectives.
- Establish a Budget: Determine a maximum budget that you are willing to spend, allowing for some flexibility in negotiations.
- Review Contract Terms: Pay close attention to SLAs, renewal clauses, and exit strategies to avoid surprises later.
- Prepare for Counteroffers: Anticipate the provider’s responses and be ready to adjust your proposals accordingly.
- Seek Legal Review: Have legal counsel review the contract before you finalize any agreement to ensure all terms are favorable and compliant.
Importance of Building Long-Term Partnerships
Establishing a long-term relationship with your SaaS provider can foster collaboration and innovation that benefits both parties. A strong partnership often leads to customized solutions that better address evolving business needs. It’s important to keep in mind the following benefits:
- Better Support: Long-term partnerships typically result in improved support from vendors, as they become more familiar with your organization’s specific needs.
- Priority Access to New Features: Partners often receive early access to new features and updates, allowing them to stay ahead of the competition.
- Flexibility in Pricing: Vendors may offer preferential pricing or discounts for renewals and expansions to loyal customers.
- Joint Development Opportunities: A strong relationship can lead to collaborative development efforts that create tailored solutions for unique business challenges.
FAQ Explained
What are the main SaaS pricing models?
The main SaaS pricing models include tiered pricing, flat-rate pricing, and per-user pricing, each catering to different business requirements.
How does customer size influence SaaS pricing?
Customer size can greatly impact SaaS pricing as larger enterprises often negotiate for better rates due to higher usage and potential long-term contracts.
What factors should be considered when negotiating SaaS pricing?
It’s essential to consider factors like service features, implementation costs, and the potential for future scalability when negotiating SaaS pricing.
How can customer feedback shape pricing strategies?
Customer feedback can provide insights into perceived value and satisfaction, influencing adjustments in pricing strategies to better meet market demands.
What future trends may impact SaaS pricing?
Emerging trends such as usage-based pricing and advancements in AI may significantly alter current SaaS pricing strategies by focusing on customer needs and consumption patterns.